






a.Energy efficient appliances usage are replacing conventional appliances
 |
|

|

|
| For example, replacing traditional T8 lighting fixtures with high efficiency T5 lighting fixtures, and also replacing the emergency exit lighting with LED lights. | |
Description:
Take the library lighting fixtures as an example, as there is a large quantity of lights and the library opening hours is up to 98 hours per week, replacing the existing lightings with high efficiency T5 lights can not only improve lighting quality, but also achieve energy conservation. The replacement of 2,347 40W and 20W traditional T8 lights in the library and the gymnasium can achieve an annual power saving of 280,000 kWh, which results in $850,000 in electricity savings and reduces CO2 emission by approximately 152 tons per year.
b. Smart Building implementation

|
|
|
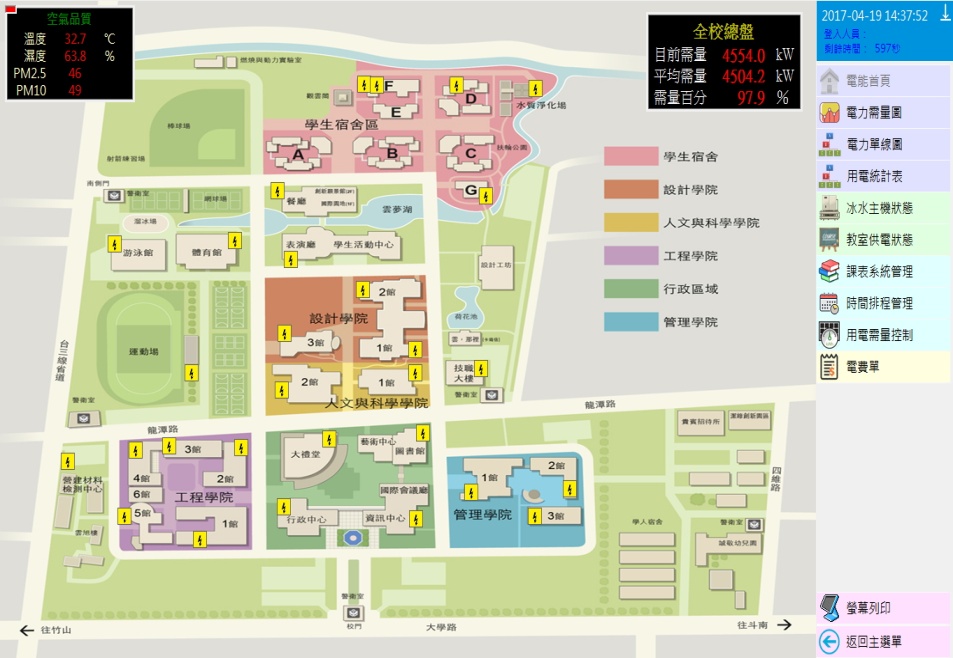
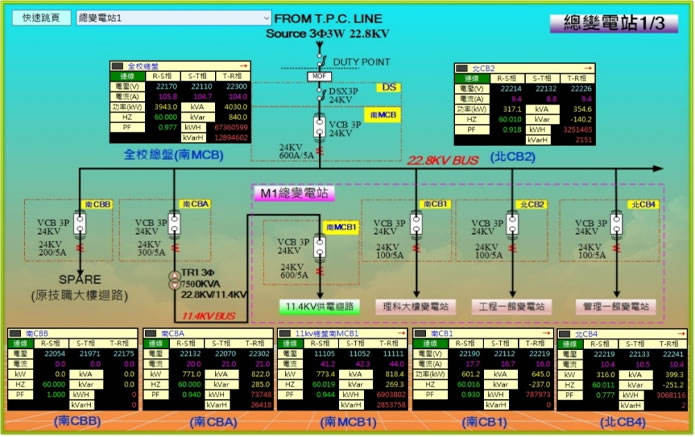
Smart Cloud Management System |
Electricity of Substation Record System |
|
Smart Grid Control Systems |
|
|
Example of Smart Building Implementation |
|
Description:
By adopting the principle of low-carbon and energy conservation, internet and cloud technologies are applied based on empirical field specifications and user requirements, a web-based platform is used for the integration and smart-management of energy, water resources, campus management and security and hazard prevention. Power consumption and demand monitoring are recorded at real-time in order to understand the power consumption status of each building.
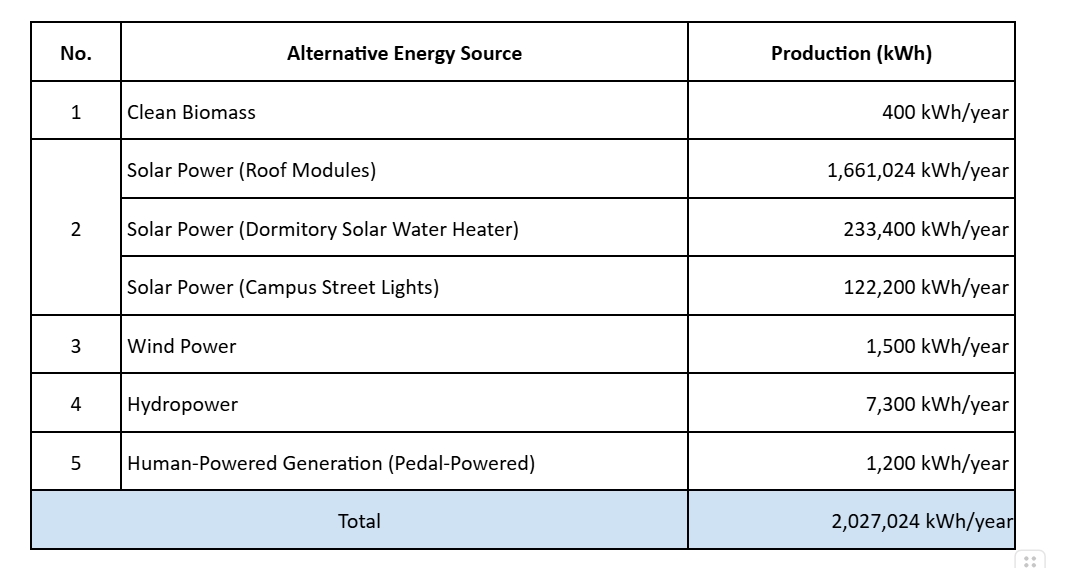
c. Renewable energy produce inside campus(2025)
|
|
Renewable energy sources and its capacity (in kilowatt-hour) |
YunTech currently employs four types of alternative energy sources on campus, including solar, wind, hydro, and combined heat and power (CHP). Among these, solar energy is the primary alternative energy source. Here are the details:
Solar Energy:
(1) Solar Power Generation: Solar photovoltaic power generation facilities are installed on the
rooftops of various buildings, maximizing the university's assets. The first phase had an installed
capacity of 495.88 kWp and has been generating an average of 512,000 kWh per year since 2013. The
second phase has an installed capacity of 698.27 kWp and has been generating an average of 948,216
kWh per year since 2019.
(2) Solar Hot Water: Solar hot water systems are installed on the rooftops of student dormitories, serving in conjunction with combined heat and power systems.
(3) Solar Street Lights: Solar street lights are installed in campus squares and open areas, effectively reducing electricity consumption
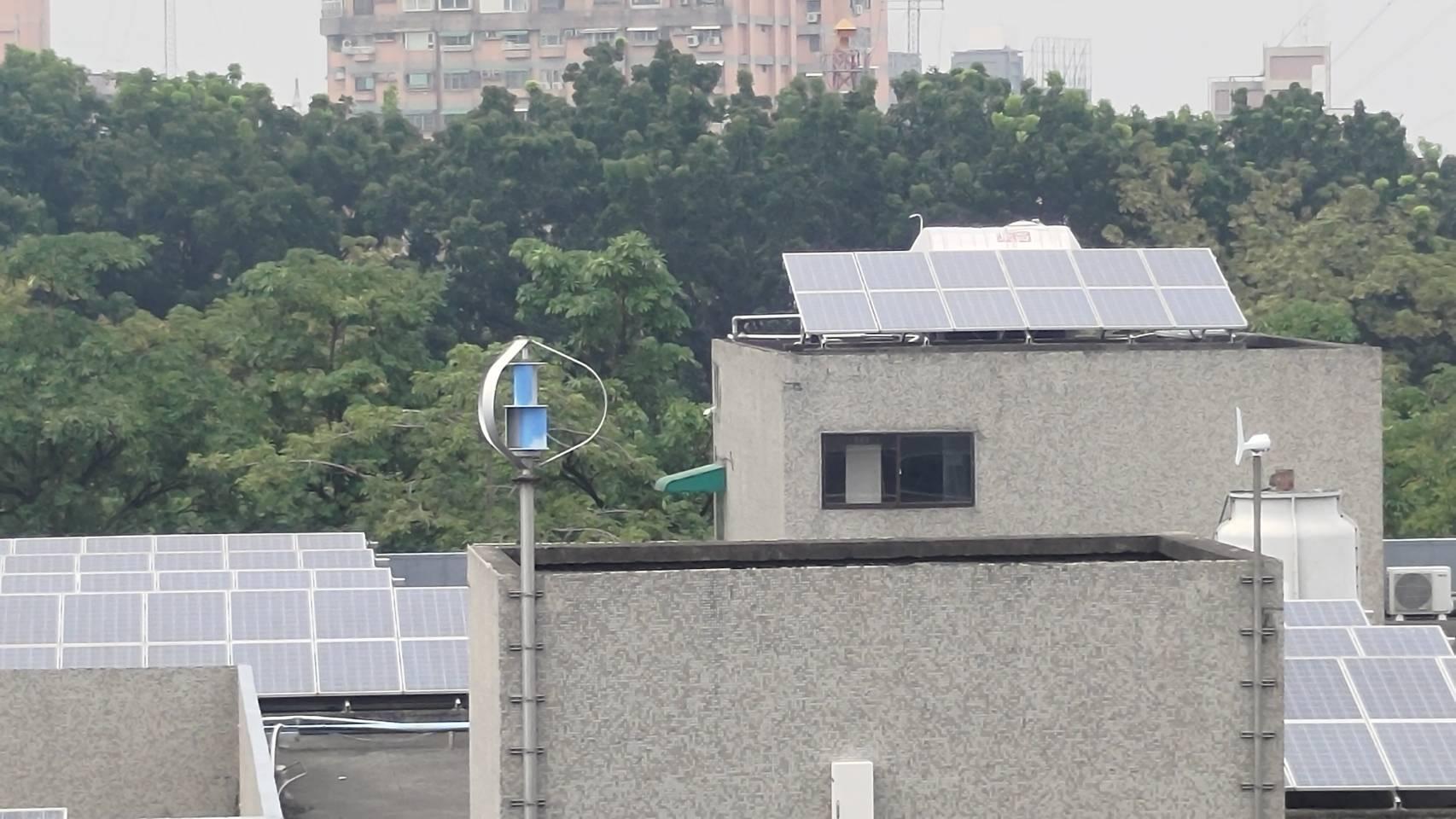
Wind Power Generation:
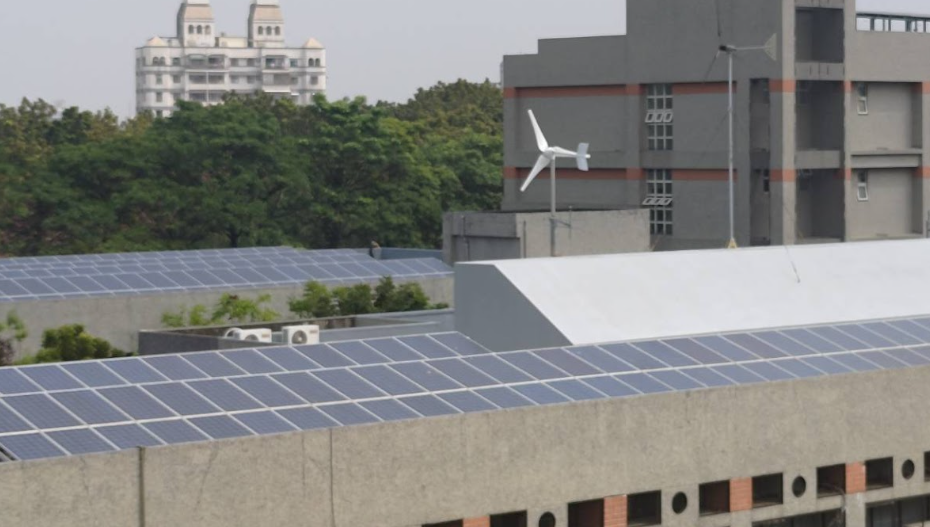
Wind power generation systems are installed on the rooftop of the Engineering Building 1, working in
tandem with energy storage systems and used for building landscape lighting.
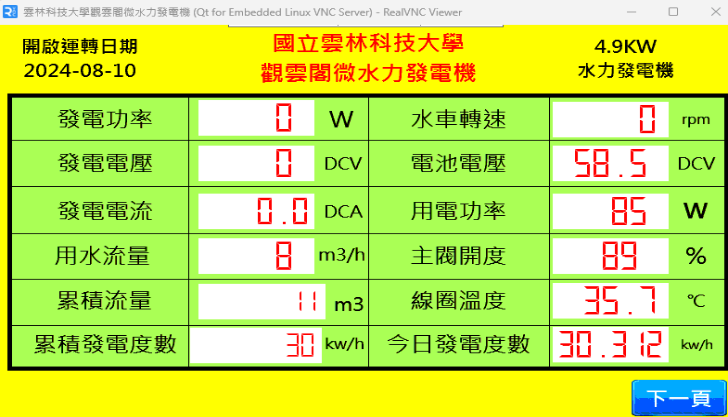
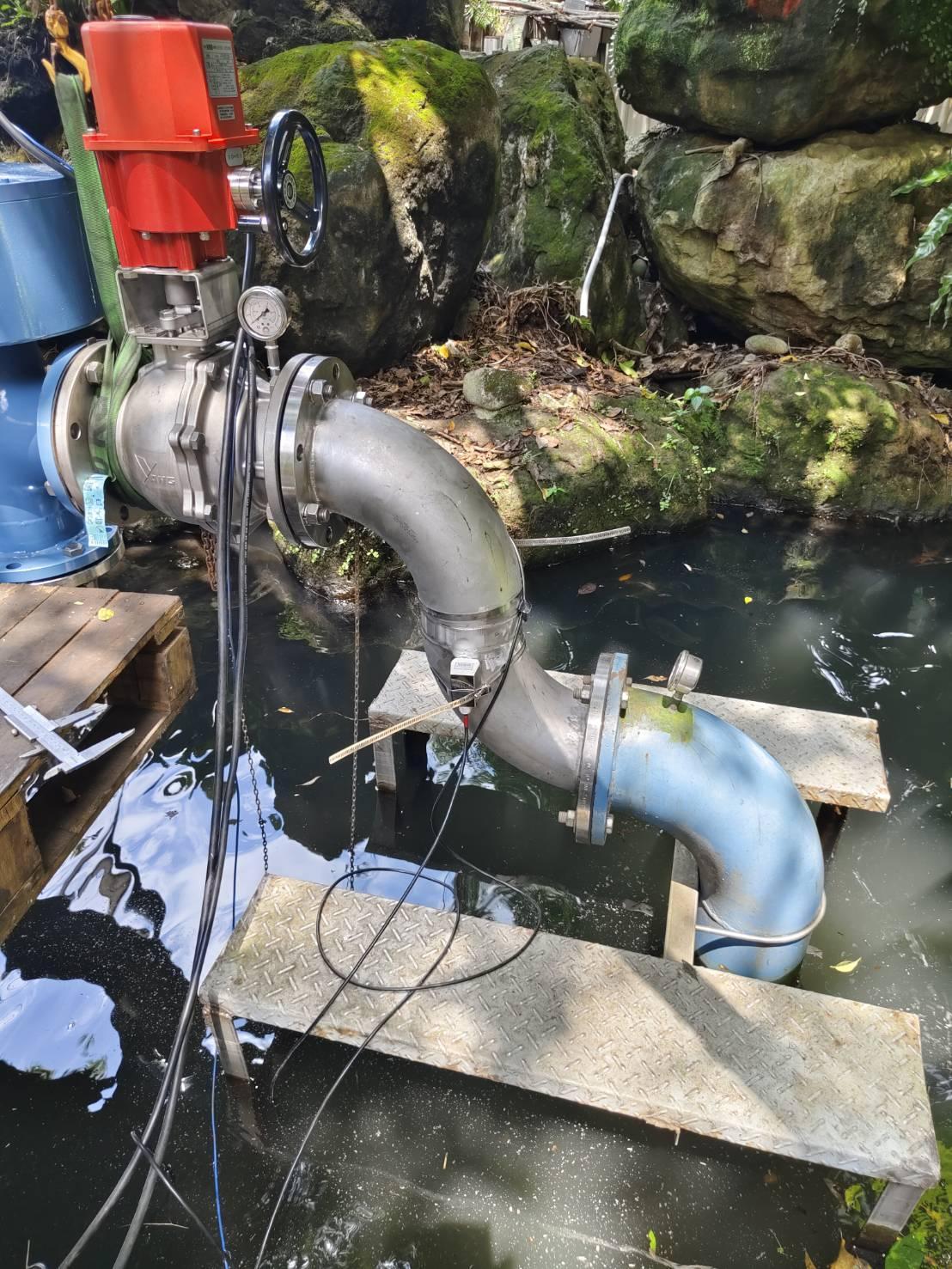
Hydro Power Generation:
Hydro power generation facilities are set up downstream of campus water channels, complemented
by energy storage systems, and used for perimeter lighting around landscape ponds.
Combined Heat and Power (CHP):
Combined heat and power systems are installed in student dormitories, working in conjunction with
rooftop solar hot water systems."

|
|
Solar Power Generation (Engineering Building, Administration Building, YunTai Performing Arts Hall, Information Center) |
 |
 |
|
Solar Power Generation (College of Management) |
Solar Power Generation (Industry-Academia Collaboration Building) |
 |
 |
|
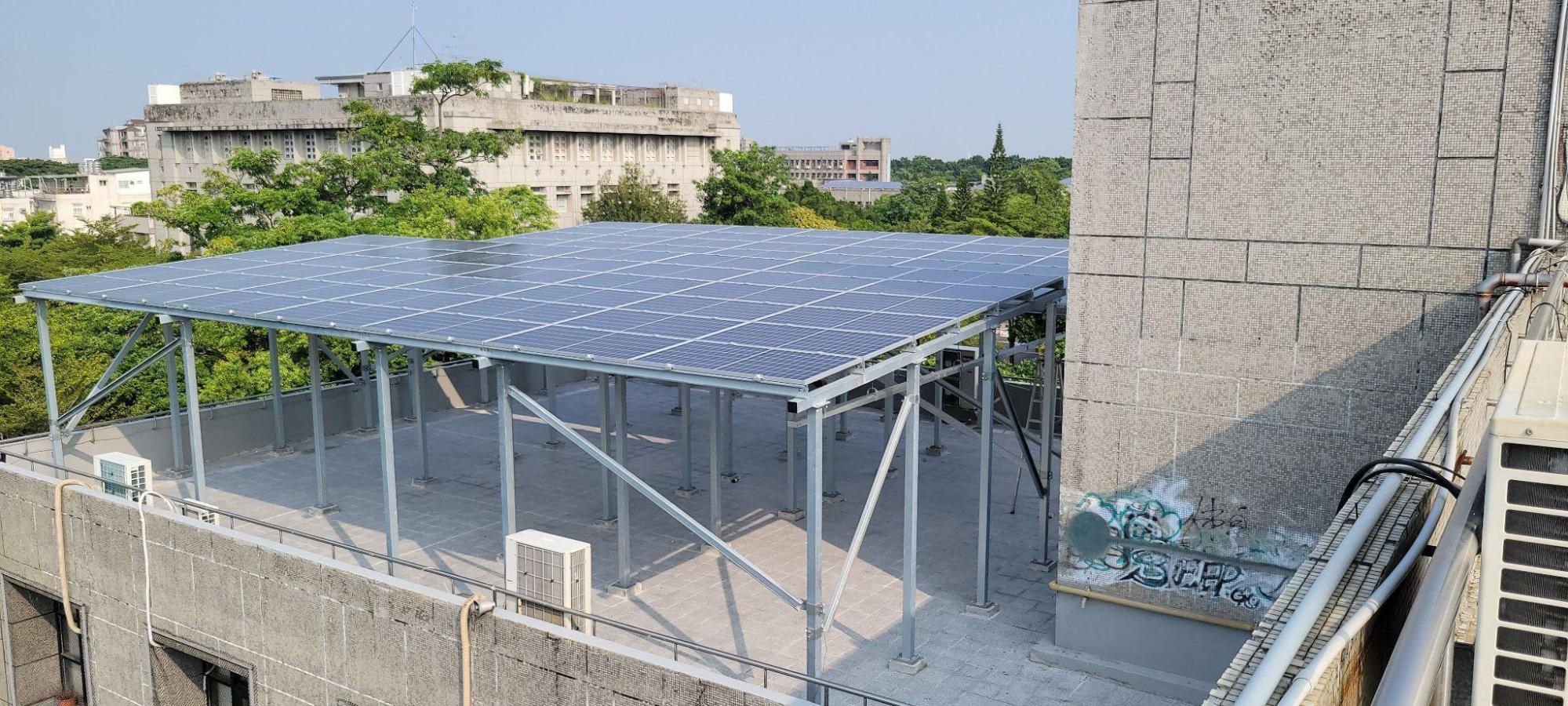
Ground-Mounted Solar Photovoltaic System (Engineering Building 1) |
Canopy-Mounted Solar Photovoltaic System (Design Building 1) |
 |
 |
|
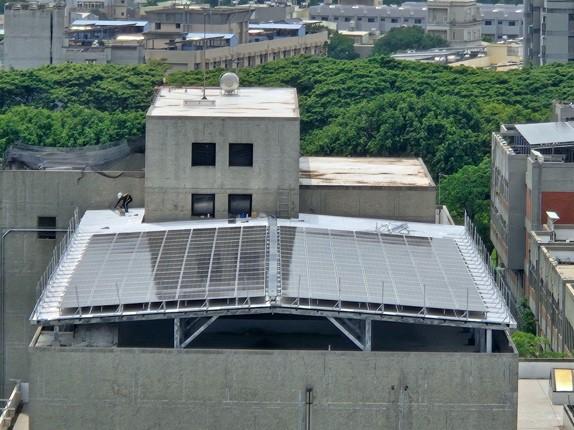
Aerial View of Solar Panels on the Library Roof |
Upward View of Solar Panels on the Library Roof |
 |
 |
|
Solar Power Generation Meter |
Solar Power Generation Meter |
 |
 |
|
Solar Water Heaters in Student Dormitories |
Solar Water Heaters in Student Dormitories |
 |
 |
|
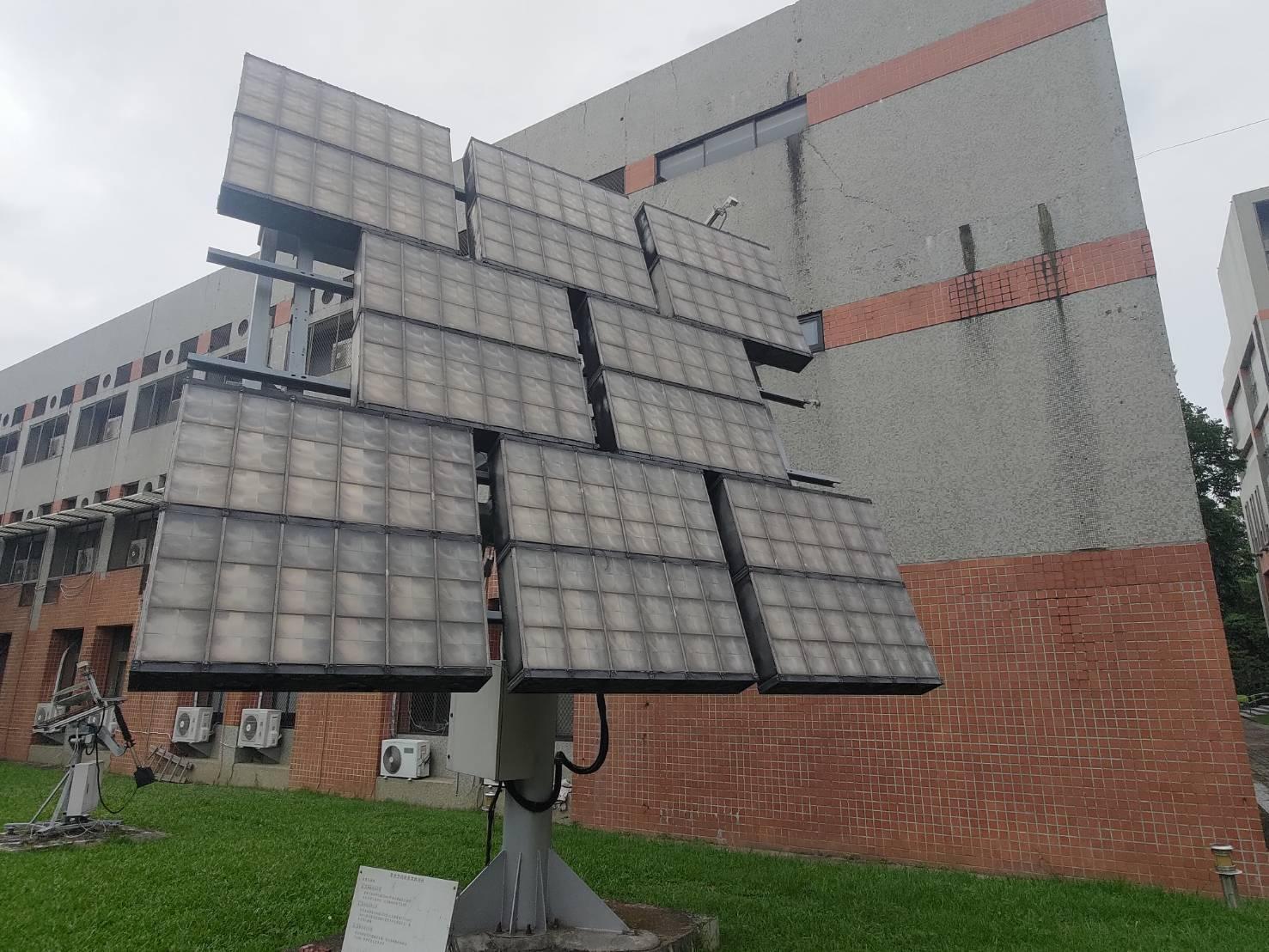
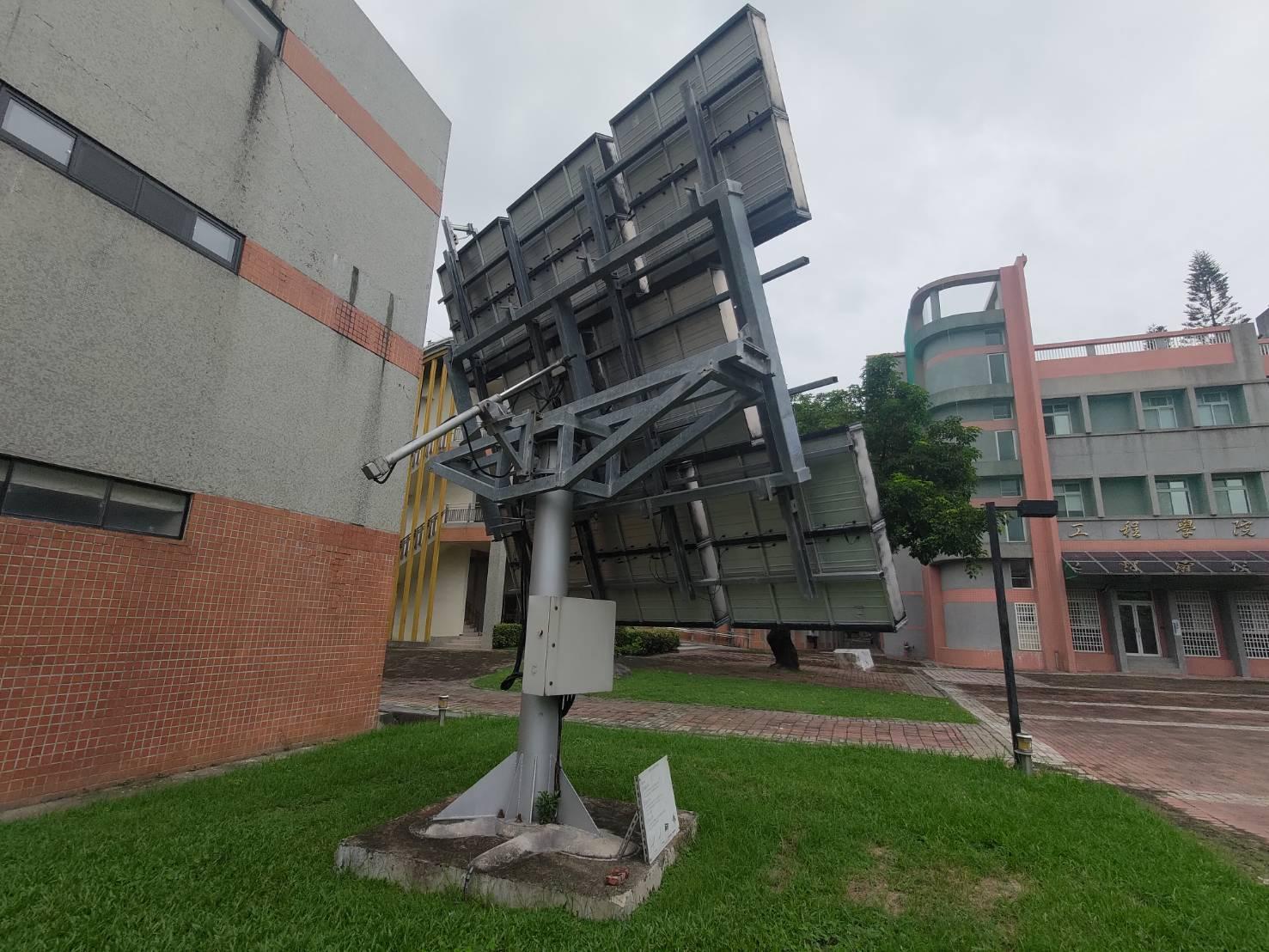
Solar Tracking System (Utilizes the angle of sunlight to automatically adjust the solar module's angle for improved energy generation efficiency.) |
|


|

|

|
|
Solar Street Lights |
Solar Street Lights |
|

|


|
|
Wind Power Generation System Installed on the Roof of Engineering Building 1 |
Wind Power Generation |

|
|
|

|

|
|
Micro-Hydropower Generation at the Guan-Yun Pavilion Building |

|

|
|
Collaboration with Government Units (Agricultural Committee, Ministry of Agriculture) to Establish Micro-Hydropower Generation in Irrigation Channels (Upstream Generation Unit) |
Collaboration with Government Units (Agricultural Committee, Ministry of Agriculture) to Establish Micro-Hydropower Generation in Irrigation Channels (Downstream Generation Unit) |
 |
 |
|
Human-Powered Generation (Pedal-Powered Electricity Generation) |
Human-Powered Generation (Pedal-Powered Electricity Generation for Lighting) |
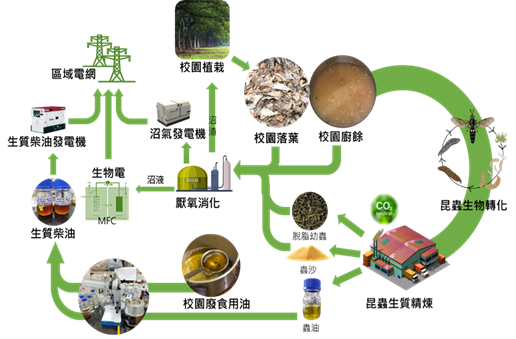 |

|
|
Biomass Energy Grid |
Biomass Energy (Converting Waste Gas Energy into Electricity to Illuminate Bulbs for Lighting) |
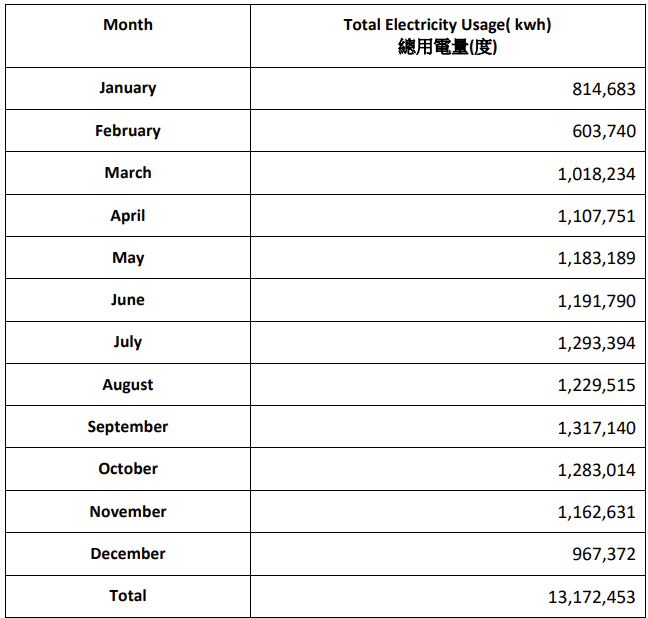
d. Electricity usage per year (in kilo watt hour)
 |

|
|
Example of Total Electricity Usage (All Locations) in 2021-2024 |
Description:
The total electricity consumption of National Yunlin University of Science and Technology in 2024 was 13,316,256 kWh. The electricity is mainly used for air conditioning, lighting, and teaching and research equipment. The chart above shows the monthly electricity consumption trend from 2021 to 2024.
• The total electricity consumption for 2024 was 13,316,256 kWh.
• The total population on campus is 11,478 (10,253+ 1,225 = 11,478).
• The total electricity consumption divided by the total campus population equals 1160.155 kWh (13,316,256 / 11,478 = 1,160.155), which is greater than 600 - 1,500 kWh.
e. Elements of green building implementation as reflected in all construction and renovation policy
 |
 |
|
Design Building 3 |
Engineering Building 5 |
 |
 |
|
Management Building 3 |
Dream Hub Building |
 |
 |
|
Prove of green building
|
Prove of green building
|
 |
 |
|
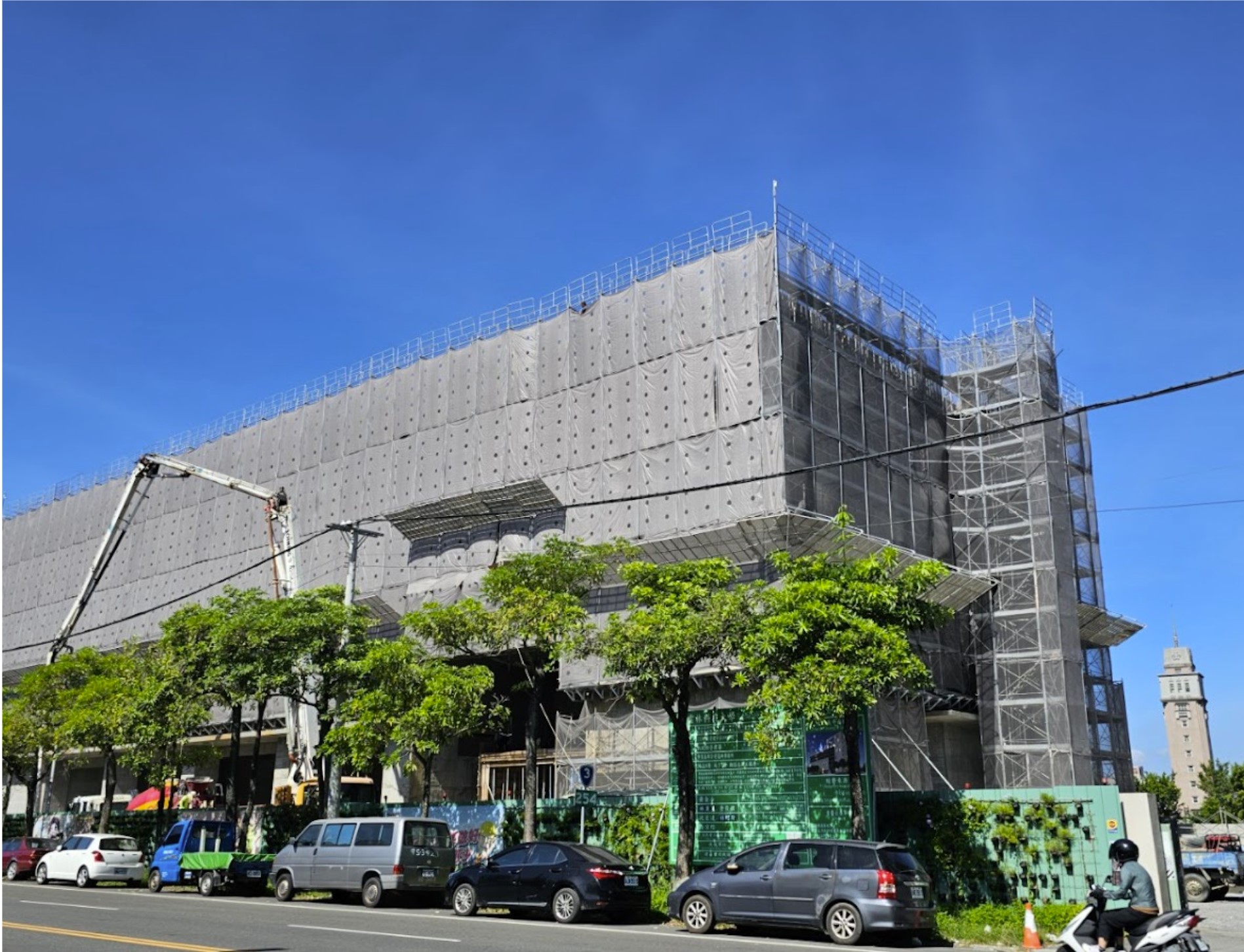
Future Scien-Tech Applying Building
|
Prove of pre-green building
|
Description:
YunTech comprises a total of 41 school buildings, one of which is currently under construction. Of these, four were constructed after the year 1999, with project costs exceeding 50 million, thus making them eligible to apply for Green Building Labels. Presently, three buildings have been awarded Green Building Labels, including the Management Building 3, Design Building 3, and Engineering Teaching Building. Furthermore, the Industry-Academic-Research Building has already obtained the Diamond-Level Green Building Candidate Certificate, boasting a 100% acquisition rate. We have provided available rooftops, while the manufacturer has contributed capital to establish an exemplary model of academic and industrial collaboration. Rental Duration: From June 12, 2012, to May 11, 2032. Established Capacity: 1.2 Megawatt Peak (MWP), with Phase 1's capacity established at 496 kWp. Power Generation: The energy generation for the contract year is estimated to reach 1.22 MW, with an annual energy generation upon completion projected at 600 kWh. Additionally, the added effect of roof insulation contributes to energy efficiency and boosts the total rental income, which amounts to approximately 15 million dollars.Furthermore, the Future Science and Technology Application Building, designed in 2021, has also obtained a Green Building Candidate Certificate. The campus buildings at National Yunlin University of Science and Technology incorporate energy-efficient architectural envelopes and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems designed to reduce the reliance on air conditioning. They are constructed based on the principles of natural ventilation and are equipped with wind cooling systems, optimizing the utilization of prevailing summer winds. Currently, six newly constructed buildings have received Green Building Labels, meeting the following criteria: greenery, site water retention, daily energy efficiency, carbon dioxide reduction, waste reduction, and water resource indicators. These buildings include Design Building 3, Engineering Building 5, Management Building 3, Industry-Academic-Research Building, and the Comprehensive Teaching Building. For instance, the Industry-Academic-Research Building has been honored with a Diamond-Level Green Building Candidate Certificate and an Intelligent Building Certificate. This recognition is a testament to its foundation in green building principles, incorporating smart high-tech technology, materials, and product applications to create a safer, healthier, more convenient, energy-efficient, environmentally friendly building. It serves as an ideal platform for cross-disciplinary programs like the 'Green Technology Program' and the 'Clean and Sustainable Technology Program,' providing opportunities for internships, experiential learning, as well as showcasing innovative outcomes and promoting sustainable practices. Additionally, the upcoming Future Science and Technology Application Building has obtained a Green Building Candidate Certificate in advance of its construction in 2022, and it will apply for a Green Building Label upon its completion.

